Sulfatase Contents Occurrence and importance Three-dimensional structure Human proteins containing this...
CholinesteraseAcetylcholinesteraseButyrylcholinesterasePectinesterase6-phosphogluconolactonasePAF acetylhydrolaseLipaseBile salt-dependentGastricLingualPancreaticLysosomalHormone-sensitiveEndothelialHepaticLipoproteinMonoacylglycerolDiacylglycerolPhospholipaseA1A2BCutinasePETaseAlkaline phosphataseALPIALPLALPPAcid phosphataseProstaticTartrate-resistant acid phosphatasePurple acid phosphatasesNucleotidaseGlucose 6-phosphataseFructose 1,6-bisphosphataseCalcineurinProtein phosphatasePP2AOCRLPyruvate dehydrogenase phosphataseFructose 6-P,2-kinase:fructose 2,6-bisphosphatasePTENPhytaseBeta-propeller phytaseInositol-phosphate phosphataseIMPA1IMPA2IMPA3Protein phosphataseProtein tyrosine phosphataseProtein serine/threonine phosphataseDual-specificity phosphatasearylsulfataseArylsulfatase AArylsulfatase BArylsulfatase ESteroid sulfataseGalactosamine-6 sulfataseIduronate-2-sulfataseN-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfataseRecBCDOligonucleotidaseDeoxyribonuclease IDeoxyribonuclease IIDeoxyribonuclease IVRestriction enzymeUvrABC endonucleaseRNase IIIRNase H12A2B2CRNase PRNase A1234/5RNase T1RNA-induced silencing complexAspergillus nuclease S1Micrococcal nuclease
Transmembrane proteins
EC3.1.6.-enzymesesterasesulfatesulfamatessulfotransferaseslysosomeglycolipidslysosomal storage disordersphenotypessequence homologyARSAARSBARSDARSEARSFARSGARSHARSIARSJARSKGALNSGNSIDSPIGGSGSHSTSSULF1SULF2
 Steroid sulfatase | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Sulfatase | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00884 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000917 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00117 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1auk | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1auk | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 24 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1p49 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Sulfatases EC 3.1.6.- are enzymes of the esterase class that catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters. These may be found on a range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. In the latter case the resultant N-sulfates can also be termed sulfamates.
Sulfatases play important roles in the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodelling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. Together with sulfotransferases, sulfatases form the major catalytic machinery for the synthesis and breakage of sulfate esters.
Contents
1 Occurrence and importance
2 Three-dimensional structure
3 Human proteins containing this domain
4 References
5 External links
Occurrence and importance
Sulfatases are found in lower and higher organisms. In higher organisms they are found in intracellular and extracellular spaces. Steroid sulfatase is distributed in a wide range of tissues throughout the body, enabling sulfated steroids synthesized in the adrenals and gonads to be desulfated following distribution through the circulation system. A large number of sulfatases are localized in the lysosome, an acidic digestive organelle found within the cell. Lysosomal sulfatases cleave a range of sulfated carbohydrates including sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids. Genetic defects in sulfatase activity can arise through mutations in individual sulfatases and result in certain lysosomal storage disorders with a spectrum of phenotypes ranging from defects in physical and intellectual development.
Three-dimensional structure
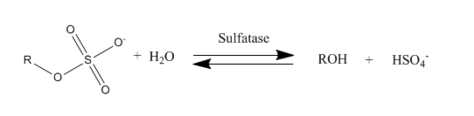
Ester sulfate hydrolysis by sulfate enzyme
The following sulfatases have been shown to be structurally related based on their sequence homology:[1][2][3]
- cerebroside-sulfatase
- steroid sulfatase
arylsulfatase A EC 3.1.6.8 (ASA), a lysosomal enzyme which hydrolyzes cerebroside sulfate;
arylsulfatase B EC 3.1.6.12 (ASB) which hydrolyzes the sulfate ester group from N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate residues of dermatan sulfate;
arylsulfatase C (ASD) and E (ASE); steryl-sulfatase EC 3.1.6.2 (STS), a membrane bound enzyme which hydrolyzes 3-beta-hydroxy steroid sulfates;
iduronate 2-sulfatase EC 3.1.6.13 (IDS), a lysosomal enzyme that hydrolyzes the 2-sulfate groups from iduronic acids in dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate;
N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase EC 3.1.6.4, which hydrolyzes the 6-sulfate groups of the N-acetyl-D-galactosamine of chondroitin sulfate and D-galactose 6-sulfate units of keratan sulfate;
N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase EC 3.10.1.1, the lysosomal enzyme that hydrolyses N-sulfo-D-glucosamine into glucosamine and sulfate;
glucosamine-6-sulfatase EC 3.1.6.14 (G6S), which hydrolyzes the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-sulfate units of heparan sulfate and keratan sulfate;
N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase EC 3.10.1.1, the lysosomal enzyme that hydrolyses N-sulfo-D-glucosamine into glucosamine and sulfate;- sea urchin embryo arylsulfatase EC 3.1.6.1;
- green algae arylsulfatase EC 3.1.6.1, which plays a role in the mineralization of sulfates; and
arylsulfatase EC 3.1.6.1 from Escherichia coli, Klebsiella aerogenes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Human proteins containing this domain
ARSA; ARSB; ARSD; ARSE; ARSF; ARSG; ARSH; ARSI;
ARSJ; ARSK; GALNS; GNS; IDS; PIGG; SGSH; STS;
SULF1; SULF2;
References
^ von Figura K, Vingron M, Schmidt B, Meyer HE, Peters C, Rommerskirch W, Rupp K, Pohlmann R, Zuhlsdorf M (1990). "Phylogenetic conservation of arylsulfatases. cDNA cloning and expression of human arylsulfatase B". J. Biol. Chem. 265 (6): 3374–3381. PMID 2303452..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Wilson PJ, Morris CP, Anson DS, Occhiodoro T, Bielicki J, Clements PR, Hopwood JJ (1990). "Hunter syndrome: isolation of an iduronate-2-sulfatase cDNA clone and analysis of patient DNA". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87 (21): 8531–8535. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.21.8531. PMC 54990. PMID 2122463.
^ Grossman AR, de Hostos EL, Schilling J (1989). "Structure and expression of the gene encoding the periplasmic arylsulfatase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii". Mol. Gen. Genet. 218 (2): 229–239. doi:10.1007/BF00331273. PMID 2476654.
External links
Sulfatases at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)- Overview at rndsystems.com
- "Annotation of the sulfatase gene family" at mad-cow.org