North Fork American River See also References External links Navigation menu39°13′04″N...
American River (California)Rivers of the Sierra Nevada (U.S.)Rivers of El Dorado County, CaliforniaRivers of Placer County, CaliforniaTributaries of the Sacramento RiverRivers of Northern CaliforniaRivers of the Sierra Nevada in California
American RiverNorthern CaliforniaSierra NevadaLake TahoeFolsom LakeSacramentoFolsom DamMountain Meadow LakeGranite ChiefTahoe National ForestColfaxLake ClementineNorth Fork Damhydraulic miningForesthill BridgeMiddle Fork American RiverAuburnSouth Fork American RiverSacramento River
| North Fork American River | |
|---|---|
 Foresthill Bridge over the North Fork | |
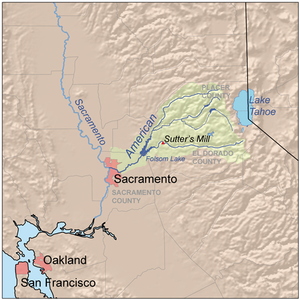 Map of the American River watershed including the North Fork | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Mountain Meadow Lake |
| - location | Sierra Nevada, Placer County |
| - coordinates | 39°13′04″N 120°16′28″W / 39.21778°N 120.27444°W / 39.21778; -120.27444[1] |
| - elevation | 7,935 ft (2,419 m) |
| Mouth | Folsom Lake |
Auburn, Placer County | |
- coordinates | 38°42′42″N 121°08′44″W / 38.71167°N 121.14556°W / 38.71167; -121.14556Coordinates: 38°42′42″N 121°08′44″W / 38.71167°N 121.14556°W / 38.71167; -121.14556[1] |
- elevation | 469 ft (143 m) |
| Length | 88 mi (142 km)[2] |
| Basin size | 996 sq mi (2,580 km2)[3] |
| Discharge | |
| - location | Rattlesnake Bar[3] |
| - average | 2,289 cu ft/s (64.8 m3/s)[3] |
| - minimum | 51 cu ft/s (1.4 m3/s) |
| - maximum | 115,000 cu ft/s (3,300 m3/s) |
The North Fork American River is the longest branch of the American River in Northern California. It is 88 miles (142 km) long from its source at the crest of the Sierra Nevada, near Lake Tahoe, to its mouth at Folsom Lake northeast of Sacramento.[2] Prior to the construction of Folsom Dam the river was about 9 miles (14 km) longer making for a total length of 97 miles (156 km).
It rises at Mountain Meadow Lake near the 9,008 ft (2,746 m) peak of Granite Chief in the Tahoe National Forest. Flowing initially northwest, the river soon swings west into a gorge, paralleling the Forest Hill Divide on the south. Big Granite Creek then the North Fork of the American River come in from the right. The canyon shallows as the river turns southwest, carving through the Sierra foothills, then turning abruptly south near Colfax. About 4 miles (6.4 km) downstream, it receives Shirttail Creek from the left then is impounded in Lake Clementine (or North Fork Lake) which is formed by the North Fork Dam, built in 1939 to contain hydraulic mining debris.[4]
Below the dam, the river bends south, passing under the Foresthill Bridge, the highest bridge in California, then receives the Middle Fork American River, its largest tributary, from the left. The valley widens as the river flows south past Auburn, soon emptying into the north arm of Folsom Lake, a reservoir formed in 1955 by the Folsom Dam. Its waters mingle with that of the South Fork American River to form the American River, a tributary of the Sacramento River.[4]
See also
- American River topics
- Auburn Dam
- California Gold Rush
Mountain Quarries Bridge — on the North Fork.
References
^ ab "North Fork American River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. 1981-01-19. Retrieved 2011-05-21..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. The National Map, accessed 2011-05-21
^ abc "USGS Gage #11434000 on the North Fork American River at Rattlesnake Bar, CA". National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 1930–1955. Retrieved 2011-05-21.
^ ab USGS Topo Maps for United States (Map). Cartography by United States Geological Survey. ACME Mapper. Retrieved 2009-10-29.
External links
North Fork American Wild and Scenic River - BLM page
